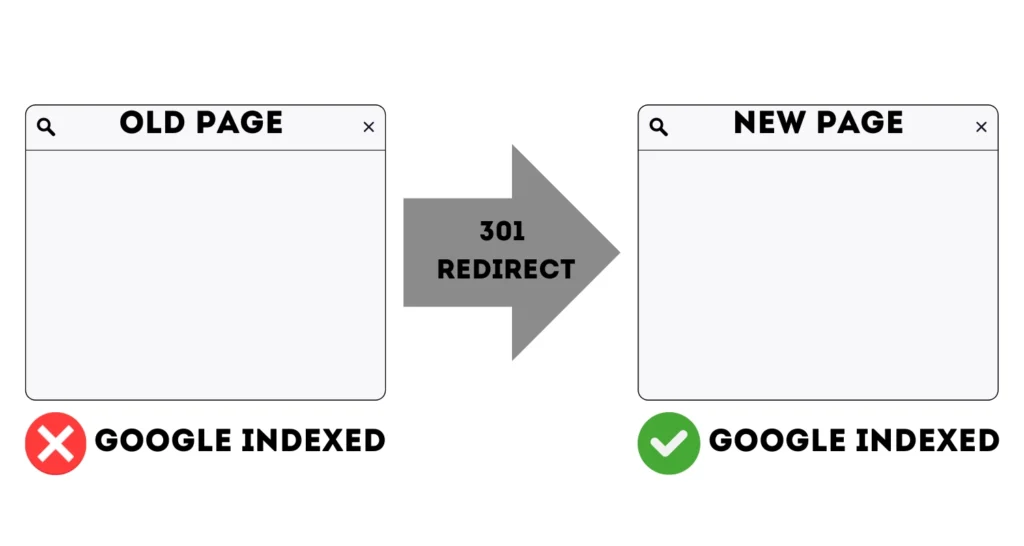
A 301 redirect (status code 301) permanently moves one URL to a different location. It’s a vital tool for website management, allowing you to guide both users and search engines to a new page when the original URL is no longer in use. Whether you’re reorganizing your site structure, migrating to a new domain, or fixing broken links, 301 redirects ensure that your site’s SEO value is preserved and users experience a seamless transition.
Why Use a 301 Redirect?
A 301 redirect ensures that users reach the intended page while also notifying search engines that the old URL has been permanently replaced by a new one. This transfer includes the “link equity” (commonly referred to as “SEO juice“) from the old URL, helping maintain your site’s rankings in search results. Unlike a 302 redirect, which is temporary, a 301 redirect ensures that search engines update their index with the new URL, preserving your site’s SEO performance.
How Do 301 Redirects Affect SEO?
Properly implementing 301 redirects is crucial for maintaining your site’s SEO health. In the past, using 301 redirects could result in a slight loss of link equity, but today, search engines like Google have improved how they handle these redirects. When done correctly, a 301 redirect passes nearly all of the original page’s SEO value to the new page.
However, misuse or overuse of 301 redirects can harm your SEO. Creating multiple redirect chains (e.g., redirecting from Page A to Page B, then from Page B to Page C) can slow down your site and confuse search engines, potentially leading to ranking drops. To avoid this, always aim to keep your redirect paths direct.
When Would it be Necessary to 301 Redirect?
Here are common scenarios where a 301 redirect is essential:
1. After Modifying a URL
If you’ve optimized or restructured a URL, a 301 redirect ensures that any existing links pointing to the old URL still lead visitors to the correct content. This is especially important if your CMS doesn’t automatically set up redirects.
2. After Creating a New Website
When launching a new website, you may need to redirect multiple URL variants (e.g., with or without “www” or switching from HTTP to HTTPS). A 301 redirect ensures that all versions of your URL lead to the same page, providing a consistent user experience and preserving your SEO efforts.
3. After Adding an SSL Certificate
Switching from HTTP to HTTPS is a crucial security step, but it changes your site’s URLs. Implementing 301 redirects from the old HTTP URLs to the new HTTPS versions ensures users and search engines access the secure site without issues.
4. Recreating a Page
When you overhaul a page’s design or content, redirecting the old URL to the new one maintains any link equity the original page had built up. This keeps your site’s SEO performance intact despite the changes.
5. Switching or Merging Domains
If you’re moving to a new domain or merging multiple domains, 301 redirects are essential. They help transfer SEO value from the old domain to the new one, ensuring that your site doesn’t lose visibility in search results.
How to Implement a 301 Redirect
Implementing a 301 redirect can be straightforward, depending on your web server setup. Here’s how to do it on some common platforms:
1. Apache (.htaccess File)
For websites running on an Apache server, you can add 301 redirects directly in the .htaccess file. Here’s how:
- Access your website’s root directory and open the .htaccess file. If it doesn’t exist, create one.
- Add the following line to redirect an old URL to a new one:
Redirect 301 /old-page.html http://www.yoursite.com/new-page.html
3. Save the file and upload it back to the server.
2. Nginx
For Nginx servers, you’ll need to modify the server configuration file:
- To access your Nginx configuration file, typically found at /etc/nginx/nginx.conf or /etc/nginx/sites-available/default.
- Add the following line inside the server block to create a 301 redirect:
server {
location /old-page.html {
return 301 http://www.yoursite.com/new-page.html;
}
}
3. Save the file and restart Nginx to apply the changes:
console.log( 'Code is Poetry' );
3. WordPress
If your site runs on WordPress, you can use a plugin to manage 301 redirects easily. One popular option is the “Redirection” plugin:
- Download and activate the “Redirection” plugin available in the WordPress plugin repository.
- Go to Tools > Redirection.
- Click on “Add New” and enter your Source URL (old URL) and Target URL (new URL).
- Save the changes.
4. cPanel
For those with cPanel access, 301 redirects can be set up through the interface:
- Log in to cPanel.
- Navigate to the “Redirects” section under the Domains heading.
- Select the type of redirect (Permanent 301), enter the old URL and the new destination URL.
- Click “Add” to save the redirect.
Best Practices for 301 Redirects
To make sure your 301 redirects work effectively and support your SEO efforts, follow these best practices:
- Test Redirects: Always test your redirects after implementation to ensure they work correctly.
- Update Internal Links: Change any internal links pointing to the old URL so that they now point to the new one.
- Minimize Redirect Chains: Avoid creating chains of redirects as they can slow down your site and confuse search engines.
- Monitor Performance: Use tools like Google Search Console to track the impact of your redirects on site performance and search visibility.
301 redirects are an essential tool for managing your website’s structure and SEO. However, they must be implemented correctly to avoid potential pitfalls like redirect chains or loss of SEO value. If you’re unsure about the best way to implement 301 redirects on your site, consulting with an SEO expert is a wise step. An expert can guide you through the process, ensuring that your redirects are set up correctly, your site’s SEO remains intact, and your users experience a seamless transition.
Have you ever faced challenges when setting up 301 redirects on your site? Share your experiences in the comments below! If you have any questions, feel free to reach out. We’re here to help you navigate the complexities of SEO and keep your site performing at its best.